Business Continuity Management:
Information Security Aspects of Business Continuity Management
This category's objective is to ensure timely resumption from, and if possible prevention of, interruptions to business activities and processes caused by failures of information systems.
Business Continuity Management Considerations
Events that trigger the implementation of a business continuity plan may have significant security implications. Depending on the event, some or all of the elements of the security environment may change. Different people may be involved in operations, at different physical locations, using similar but different machines and software which may communicate over different communications lines. Different trade offs may exist between availability, integrity, confidentiality, and accountability, with a different appetite for risk on the part of management.
Including information security in the business continuity management process
A managed process should be developed and maintained for business continuity throughout the organization, that includes information security requirements needed for the organization's business continuity.
Business continuity plans should be reviewed as an integral part of the security process. Risk assessments should consider the changing risks that appear in business continuity scenarios and the different security posture that may be established. Strategies should consider the different risk environment and the degree of risk mitigation necessary to protect the institution in the event the continuity plans must be implemented. The implementation should consider the training of appropriate personnel in their security roles, and the implementation and updating of technologies and plans for back-up sites and communications networks. These security considerations should be integrated with the testing of business continuity plan implementations.
Control includes:
- Identification of information assets involved in critical business processes
- A risk assessment that addresses likely causes and consequences of information system failures
- Identification and consideration of preventive and mitigating controls in light of these risks
- Identification of sufficient financial, technical and human resources to address the preventive/mitigating control requirements
- Development and documentation of business continuity plans and processes, including assignment of responsibilities and incorporation into the organization's general processes and structure
- Regular testing and updating of business continuity plans and processes
Business continuity and risk assessment
Events that can cause interruptions to business processes should be identified, along with the probability and impact of such interruptions and their consequences for information security.
Control includes:
- Identification of all significant risk or risk categories, including the probability and probable impact on operations in terms of scale, likely damage and recovery period
- Full involvement of owners of significant organizational assets in the assessment process
- Identification of acceptable and unacceptable losses and interruptions
- Formal documentation of the assessment's results, and a plan for regular updating to ensure completeness and currency
Developing and implementing continuity plans including information security
Business continuity plans should be developed and implemented to maintain or restore operations and ensure availability of information at the required level and in the required time, following interruptions to or failures of business processes.
Control includes:
- Identification of and agreement on all responsibilities and operational procedures
- Specification of the disaster recovery/business continuity procedures to effect recovery and restoration of business processes
- A data backup plan to ensure recovery of all data following process restoration, including the ability to replicate exact copies of data in its state prior to disruption of operations
- Specification of alternative operational procedures to follow pending completion of recovery and restoration, including methods for accessing all critical data
- Documentation of the above plan elements
- Appropriate education and awareness efforts for staff on the plan elements
- Testing and updating of the plan
Business continuity planning framework
A single framework of business continuity plans should be maintained to ensure that all plans are consistent, consistently assess information security requirements, and to identify priorities for testing and maintenance.
Control includes:
- Specification of conditions and criteria for activating the plan
- Formal assignment of responsibilities for making assessments about plan activation, choices among emergency procedures and processes, resumption procedures, etc.
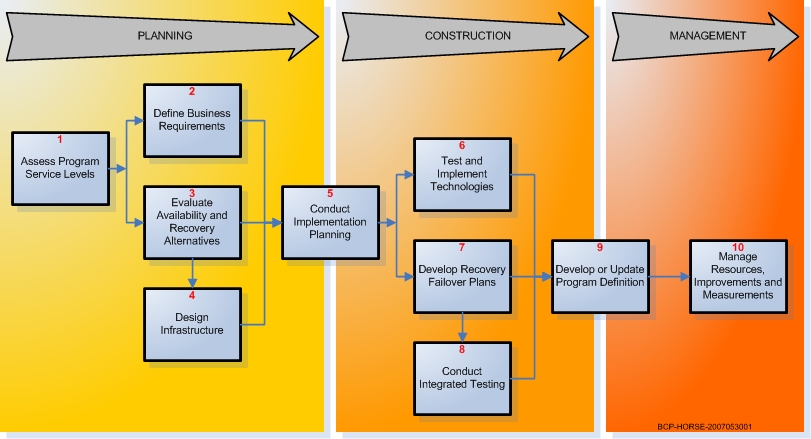
Make informed choices that reveal the right cost benefit tradeoffs for your business continuity program. Always analyzes availability and recovery alternatives, recommend a business continuity strategy that meets the defined business requirements, and provide technical solutions identifying high level cost and benefits for each alternative.
This diagram illustrates the basic decision process flow to successfully accomplish your business continuity program requirments.
Business Continuity Management Policy Samples
ISO 27002:2005 defines Business Continuity Management objectives to counteract interruptions to business and protect critical business processes from the effects of major failures or disasters. This section provides templates for Information Security standards that are required to comply with ISO Business Continuity Management objectives and support the objectives established in the Asset Protection Policy, and Threat Assessment and Monitoring Policy.
- 1. Sample ISO Availability Protection Standard
- The Availability Protection Standard is required to comply with ISO Business Continuity Management objectives and builds on the objectives established in the Asset Protection Policy by providing specific requirements for protecting the availability of information assets.
- 2. Sample ISO Threat Monitoring Standard
- The Threat Monitoring Standard is required to comply with ISO Business Continuity Management objectives and builds on the objectives established in the Threat Assessment and Monitoring Policy by providing specific requirements for periodically identifying, analyzing, and prioritizing threats to sensitive information such as health information pertaining to individuals. The Threat Monitoring Standard provides specific requirements for performing real-time intrusion detection monitoring and periodic intrusion detection analysis to detect threat and intrusion activity.
- 3. Sample ISO Incident Response Standard
- The Incident Response Standard is required to comply with ISO Business Continuity Management and builds on the objectives established in the Threat Assessment and Monitoring Policy by providing specific requirements for developing and exercising formal plans, and associated metrics, for responding to security incidents and intrusions.
IT Service Continuity Management
IT Service Continuity Management helps to ensure the availability and rapid restoration of IT services in the event of a disaster. The high level activities are Risk Analysis, Contingency Plan Testing, and Risk Management.
HORSE FACTS: Financial institutions should consider:
- Identification of personnel with key security roles during a continuity plan implementation, and training personnel in those roles.
- Security needs for back-up sites and alternate communication networks.
Testing, maintaining and re-assessing business continuity plans
Business continuity plans should be tested and updated regularly to ensure that they are up to date and effective.
Control includes:
- Testing that assures that all persons with significant responsibilities under the plan(s) are aware of and competent to perform them
- A range and frequency of testing exercises, from table-top to complete rehearsals, performed as necessary to ensure awareness and competence
- Regular reviews and updating of the plan(s) in light of testing results
See Also
ISO-27002:2005 14
HIPAA 164.308(a)(7)
JCAHO-IM:2004 2.20
PCI/DSS:2005 12.8.3
ISO-27002:2005 14.1.1
HIPAA 164.308(a)(7)(i)
ISO-27002:2005 14.1.2
HIPAA 164.308(a)(7)(ii)(E)
ISO-27002:2005 14.1.3
HIPAA 164.308(a)(7)(ii)(A-C)
HIPAA 164.312(a)(2)(ii)
ISO-27002:2005 14.1.4
HIPAA 164.308(a)(7)(i)
ISO-27002:2005 14.1.5
HIPAA 164.308(a)(7)(ii)(D)
References
- See: Continuity Management
- The “Business Continuity Planning” booklet of the FFIEC IT Examination Handbook.
- ISO 17799/27002 - Code of Practice for Information Security Management.