DS5.3:
DS 5.3 Identity Management
Control Objective:
All users (internal, external and temporary) and their activity on IT systems (business application, system operation, development and maintenance) should be uniquely identifiable. User access rights to systems and data should be in line with defined and documented business needs and job requirements. User access rights are requested by user management, approved by system owner and implemented by the security-responsible person. User identities and access rights are maintained in a central repository. Cost-effective technical and procedural measures are deployed and kept current to establish user identification, implement authentication and enforce access rights.
Applicability:
- Sarbanes-Oxley
- HIPAA
- GLBA
- PCI
- FISMA
- NIST SP 800-66
- Ditscap
- Control Exception
- User Defined
Risk Association Control Activities:
- 1. Risk: Third party service providers may not meet business, compliance and regulatory needs of the business inducing risk.
- a. SOX.1.5 A designated individual is responsible for regular monitoring and reporting on the achievement of the third-party service-level performance criteria.
- a. SOX.1.5 A designated individual is responsible for regular monitoring and reporting on the achievement of the third-party service-level performance criteria.
- 1. Risk: Third party service providers may not meet business, compliance and regulatory needs of the business inducing risk.
- 2. Risk: Third party processors create unacceptable control risks to the Company.
- a. SOX.2.0.5 Selection of Vendors for outsourced services is performed in accordance with the organization's vendor management policy.
- 2. Risk: Third party processors create unacceptable control risks to the Company.
- 3. Risk: System security may be undermined by inappropriate external system connections.
- a. SOX.3.1.3 External system connections should be used for valid business purposes only and controls should be in place to prevent these connections from undermining system security.
- 3. Risk: System security may be undermined by inappropriate external system connections.
- 4. Risk: Increased vulnerability may be exploited adversely impacting system availability, confidentiality and integrity of programs, processing and data.
- a. SOX.4.0.1 User accounts are set up individually for each employee and passwords are changed every XXX days. Default account passwords are changed.
- 4. Risk: Increased vulnerability may be exploited adversely impacting system availability, confidentiality and integrity of programs, processing and data.
- 5. Risk: Data may be lost, altered, or corrupted.
- a. SOX.4.1.3 Database change controls should restrict unauthorized manipulation to preserve production data structures.
- 5. Risk: Data may be lost, altered, or corrupted.
- 6. Risk: Users may have inappropriate access to the application system.
- a. SOX.5.1.1 Access to the application system is appropriately restricted to prevent unauthorized activity.
- 6. Risk: Users may have inappropriate access to the application system.
- 7. Risk: Segregation of duties may be compromised and unauthorized activity may occur.
- a. SOX.7.1.1 Access to particular functions within applications (e.g., approving payment of vendors) should be appropriately restricted to ensure segregation of duties and prevent unauthorized activity.
- 7. Risk: Segregation of duties may be compromised and unauthorized activity may occur.
- PCI.8.1: Identify all users with a unique username before allowing them to access system components or cardholder data.
- PCI.8.2: Employ at least one of the methods below, in addition to unique identification, to authenticate all users: Password, Token devices (e.g., SecureID, certificates, or public key), Biometrics.
- PCI.8.3: Implement 2-factor authentication for remote access to the network by employees, administrators, and third parties. Use technologies such as RADIUS or TACACS with tokens, or VPN with individual certificates.
- PCI.8.4: Encrypt all passwords during transmission and storage, on all system components.
Implementation Guide:
Process Narrative
Insert a description of the process narration that is applicable to the existing control statement this narrative refers to.
Process Illustration
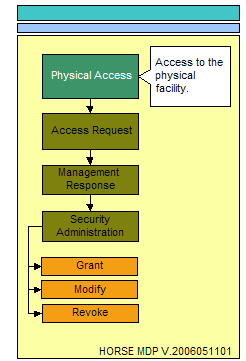
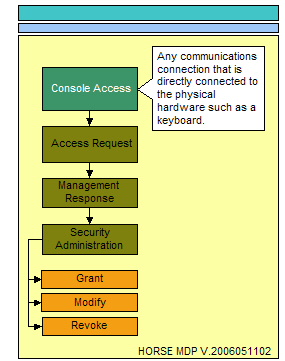
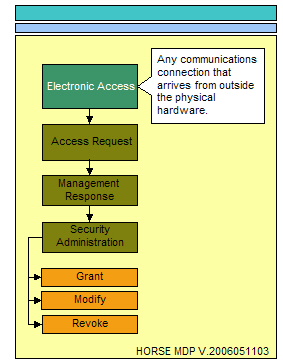
The essence of access can only come in the form of physical access, electronic access, and local console access. The physical location that surrounds critical data stores and the physical locations where electronic or local console access mechanisms exist providing a conduit to critical data stores must be considered. The following three illustrations represent the process flow for administering access to any resource.
Physical access can be best described as the physical location that surrounds critical data stores and the physical locations where electronic or local console access mechanisms exist providing a conduit to these critical data stores.
Console access can be best described as the location that has physical devices such as keyboards or USB ports providing a locally connected mechanism to access the system hosting critical data stores.
Electronic access is best described as the various mechanisms used to access critical data stores and systems electronically. An example of this would be the Ethernet system connection, serial port or wireless access port that may be used to access the system hosting critical data stores. This connection is the most difficult to control due to the fact that there are so many ports, protocols, applications, and methodologies available to connect to systems electronically from anywhere in the world.
Control Commentary
Insert a description of the control that is applicable to the existing control statement this commentary refers to.
Control Exception Commentary
Insert a description of the control exception that is applicable to the existing control statement this commentary refers to.
Evidence Archive Location
Insert Evidence Description Here.
Control Status and Auditors Commentary
Describe the condition of the applicable control and its effectiveness. Set the color icon to a redlock.jpg, yellowlock.jpg or greenlock.jpg.
File:Redlock.jpg
Remediation Plan
Insert remediation plan, applicability, or any information that indicates what needs to be done.
Supplemental Information: